Rotherwood Farming
Hold their 4th on farm APR bull Helmsman auction sale
Offering 17 2 year old and 2 3 year old and 1 4 year old bull
To be held on the property "Rotherwood"
342A Victoria Valley Rd, Ouse at 1pm 27th August 2015
Inspection: 11 am ( bbq & refreshments available )
Contact:
Bernard Brain - 6287 1309 or 0428 87109
Helen Sproule - 0448 871 313
Roberts Ltd:
Rebecca Oakley - 0408 146 033
Tim Woodham 0418 323 425
Jock Gibson 0418 133 595
History of the "Rotherwood" herd
The herd began in the late 1950's with 26 heifers bought from “Glenelg” Gretna. In 1963 we started weighing calves, calculating weight ratios, and culling cows whose calves under-performed- we were probably the first Angus herd in Tasmania to do performance recording. Over the next few years sires were purchased from Tasmania, Victoria and New Zealand with variable results. Some performed well, but others not as well as home –bred sires. Others had to be culled due to their foot problems along with their progeny.
In the early 1970's an Agricultural Officer suggested setting up a nucleus breeding scheme; with 6 breeders suppling their best heifers to the nucleus and receiving a set ratio of bulls in return. Rotherwood was chosen to host the nucleus herd. The aim was to have a regular supply of bulls of the type the members desired-which would improve their herds, at a reasonable cost. The bulls to be used in the nucleus, or supplied, were chosen at a meeting in June, when the new heifers arrived. This worked well for 33 years until it was wound up because of a drop in the number of herds, due to owner retirement, and property or herd sale, when the gene pool became too small. It had initially been 2000 cows.
The herd enrolled in Breedplan from the beginning, as an Angus Performance Register herd. At the time our 200 and 600day weight EBV's were about 20% above breed average until the influence of North American genetics occurred. Our aim is to keep birth weights low, while maximizing 600 day weights with improved muscling and keeping our reputation for docile cattle with good conformation. Surplus cows and heifers (EU accredited) have been sold at the Powranna autumn commercial cattle sale.
After many years selling bulls privately we decided to move to a helmsman auction system in 2012. We felt that it would provide the fairest method of selling bulls by auction. The sales have worked well for us and buyers were happy with the type of auction system that we used, as it gave prospective purchasers time to go back and look at the bulls during the auction, and change their preferred animal if so desired.
RELEVANT TERMS
- AMFU, CAFU, NHFU, and DDFU - untested for the genetic disorders but believed to be free.
- AMF, CAF, NHF, and DDF - tested for genetic disorders and are free.
- AM% - the _% probability that the animal is an AM carrier.
- NH% - the _% probability that the animal is a NH carrier.
- CA% - the _% probability that the animal is a CA carrier.
- DD% - the _% probability that the animal is a DD carrier.
- Calving ease direct (CEM or CEdir) and Calving ease Daughters (CED or CEDtrs) - genetic estimate of ease of dam or daughter as 2yo heifers to calve without assistance
- Birth weight (Bwt) - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in calf birth weight.
- 200 day weight - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in liveweight at 200 days of age.
- 400 day weight - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in liveweight at 400 days of age.
- 600 day weight - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in liveweight at 600 days of age.
- Mature weight (Mwt) - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in cow weight at 5 years of age.
- Milk - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in milk production, expressed as variation in 200-day weight of daughter's calves.
- Scrotal size (SS) - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in scrotal circumference at 400 days of age.
- Days to calving (DOC) - Estimates of the genetic differences in female fertility, expressed as the number of days from the start of the joining period until subsequent calving.
- Carcase weight(Cwt) - Estimates of the genetic differences between animals in carcase weight, adjusted to 650 days of age.
AUSTRALIAN ANGUS SELECTION INDEXES
There are four standard selection indexes calculated for Australian Angus animals. These are:
- Angus Breeding Index (ABI)
- Domestic Index (DOM)
- Heavy Grain Index (GRN)
- Heavy Grass Index (GRS)
The Angus Breeding Index - is a general purpose selection index that is suitable for use in the majority of commercial beef operations, whereas the Domestic, Heavy Grain and Heavy Grass selection indexes are specific to beef operations targeting a defined production system and market endpoint.
Angus Breeding Index - estimates the genetic differences between animals in net profitability per cow joined in a typical commercial self replacing herd using Angus bulls. This selection index is not specific to a particular production system or market end-point, but identifies animals that will improve overall profitability in the majority of commercial grass and grain finishing beef production systems. This selection index is particularly suited to commercial producers who sell progeny into different markets, or to seedstock producers supplying bulls to commercial clients who produce for a range of different production systems and market end points.
Domestic Index - estimates the genetic differences between animals in net profitability per cow joined in a commercial self replacing herd targeting the domestic supermarket trade. Steers are assumed to be finished using either grass, grass supplemented by grain or grain (eg. 50 – 70 days) with steers slaughtered at 490 kg live weight (270 kg carcase weight with 12 mm P8 fat depth) at 16 months of age. Daughters are retained for breeding and therefore maternal traits are of importance. Emphasis has been placed on eating quality and tenderness to favour animals that are suited to MSA requirements.
Heavy Grain Index - estimates the genetic differences between animals in net profitability per cow joined in a commercial self replacing herd targeting pasture grown steers with a 200 day feedlot finishing period for the grain fed high quality, highly marbled markets. Steers are assumed to be slaughtered at 760 kg live weight (420 kg carcase weight with 30 mm P8 fat depth) at 24 months of age. Daughters are retained for breeding and therefore maternal traits are of importance. There is a significant premium for steers that exhibit superior marbling.
Heavy Grass Index - estimates the genetic differences between animals in net profitability per cow joined in a commercial self replacing herd targeting pasture finished steers. Steers are assumed to be slaughtered at 620 kg live weight (340 kg carcase weight with 12 mm P8 fat depth) at 22 months of age. Daughters are retained for breeding and therefore maternal traits are of importance. Emphasis has been placed on eating quality and tenderness to favour animals that are suited to MSA requirements.
Accuracy (Acc) - Provides an indication of the reliability of an EBV. As more performance information becomes available on an animal (or its progeny, or relatives) then the accuracy of its EBVs for particular traits will increase.
RECESSIVE GENETIC CONDITION
INFORMATION FOR BULL BUYERS
This is information for bull buyers about the undesirable genetic conditions, Arthrogryposis
Multiplex (AM), Neuropathic Hydrocephalus (NH), Contractural Arachnodactyly (CA) and Developmental Duplications (DD).
Putting Undesirable Genetic Recessive Conditions in Perspective
All breeds of cattle, in fact all mammals including humans, have undesirable genetic
conditions. Fortunately, advances in molecular genetics have facilitated the development of
DNA tests for their management. Angus Australia is at the forefront of development of
strategies to manage undesirable genetic conditions and Angus members are leading the
industry with their uptake of this technology.
What are AM, NH CA and DD?
Arthrogryposis means 'curved or hooked joints'. Multiplex indicates there are multiple
abnormalities associated with the condition. Animals with the NH condition have a large
head. Both AM and NH affected calves are not born alive. Whilst; calves affected by CA are
born alive and can reproduce, muscle contractures restrict the movement of joints,
particularly in the hind legs. Abnormal muscle contracture decreases dramatically as a calf
ages, while muscle development always remains poor. DD causes duplication of limbs, etc.
How are the conditions inherited?
Research in the U.S. and Australia indicates that AM, NH CA and DD are simply inherited
recessive conditions. This means that a single pair of genes controls the condition. For this
mode of inheritance two copies of the undesirable gene need to be present before the
condition is seen; in which case you may get an abnormal calf. A more common example of
a trait with a simple recessive pattern of inheritance is black and red coat colour.
Animals with only one copy of the undesirable gene (and one copy of the normal form of the
gene) appear normal and are known as “carriers”.
What happens when carriers are mated to other animals?
Carriers, will on average, pass the undesirable gene form to a random half (50 %) of their
progeny. When a carrier bull and carrier cow is mated, there should be a 25% chance that the progeny
produced will have two normal genes. There should be a 50% chance that the mating will
produce a carrier. However, there could be a 25% chance that the progeny have two copies
of the undesirable gene.
Key point: The number of reported observations of AM, NH CA and DD calves is very low and there is certainly no need for panic.
Key point: With today's DNA tools undesirable genetic conditions can be managed!
If animals tested free of the undesirable gene are mated to carrier animals the condition will
not be expressed at all. All calves will appear normal, but approximately half (50%) could be
expected to be carriers.
How is the AM NH CA and DD status of animals reported?
A DNA-based test has been developed that can be used to determine whether an animal is a
carrier or free of the AM, NH CA or DD gene.
Angus Australia uses sophisticated software to calculate the probability of (all untested)
animals to be a carrier. The software uses the test results of any relatives in the calculations
and the probabilities may change as new results for additional animals become available.
The genetic status of animals is being reported using five categories:
- AMF Tested AM free
- AMFU Based on pedigree AM free – Animal has not been tested
- AM__% _% probability the animal is an AM carrier
- AMC Tested AM-Carrier
- AMA AM-Affected
For NH CA or DD, simply replace AM in the above table with NH CA or DD.
Registration certificates and the Angus Australia (AA) web-database display these codes.
This information is displayed on the animal details page and can be accessed by conducting
an “Animal Search” from the Angus website or looking up individual animals listed for sale in
a sale catalogue.
Implications for Commercial Producers
Your decision on what genetic condition statuses are acceptable will depend on the genetics
of your cow herd (which bulls you previously used), whether you have a straightbreeding or
crossbreeding enterprise and whether some female progeny will be retained as breeders.
Angus Australia seedstock breeders are being proactive and transparent in managing these
genetic conditions, endeavouring to provide the best information available. The greatest risk
to the commercial sector from undesirable genetic recessive conditions comes from
unregistered bulls with unknown genetic background. The DNA testing that Angus Australia
seedstock producers are investing in provides buyers of registered Angus bulls with
unmatched quality assurance.
For further information contact Angus Australia's Breed Development and Innovation Manager at (02) 6773 4602.
Key point: For the condition to be expressed the undesirable gene needs to be present on both sides of the pedigree and both the sire and dam need to be a carrier.
Key point: The genetic status of an animal is subject to change and will be reanalysed And adjusted each week as DNA test results of relatives are received.
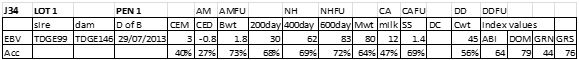
LOT 1
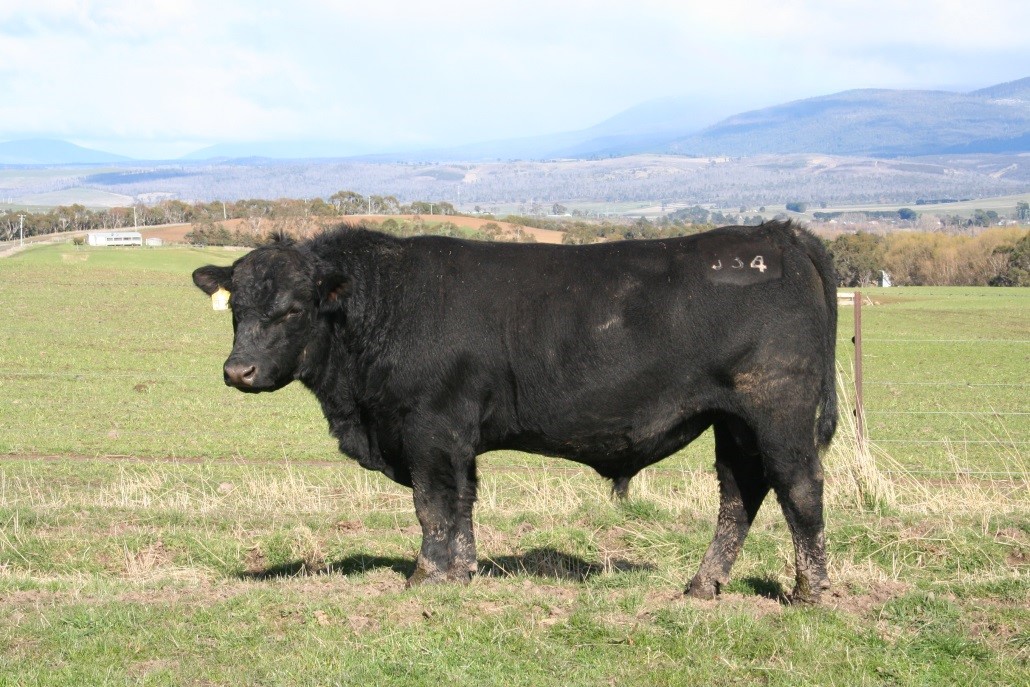

Price........... Purchaser..............................
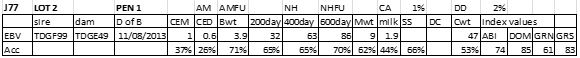
LOT 2
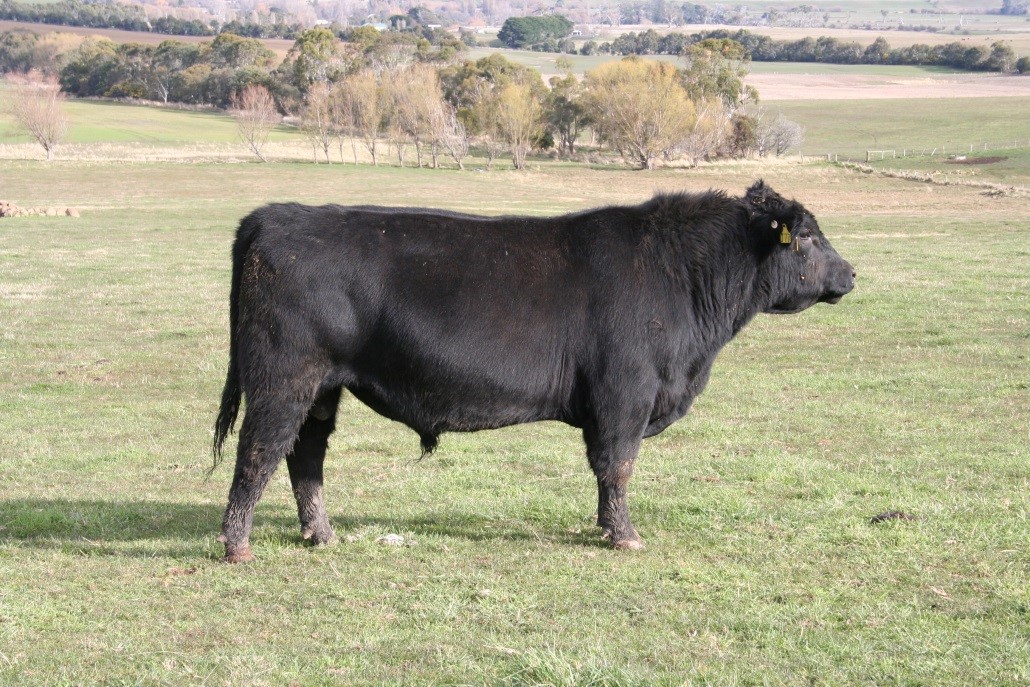

Price........... Purchaser..............................
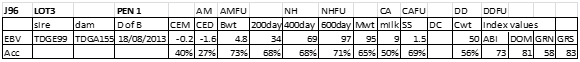
LOT 3
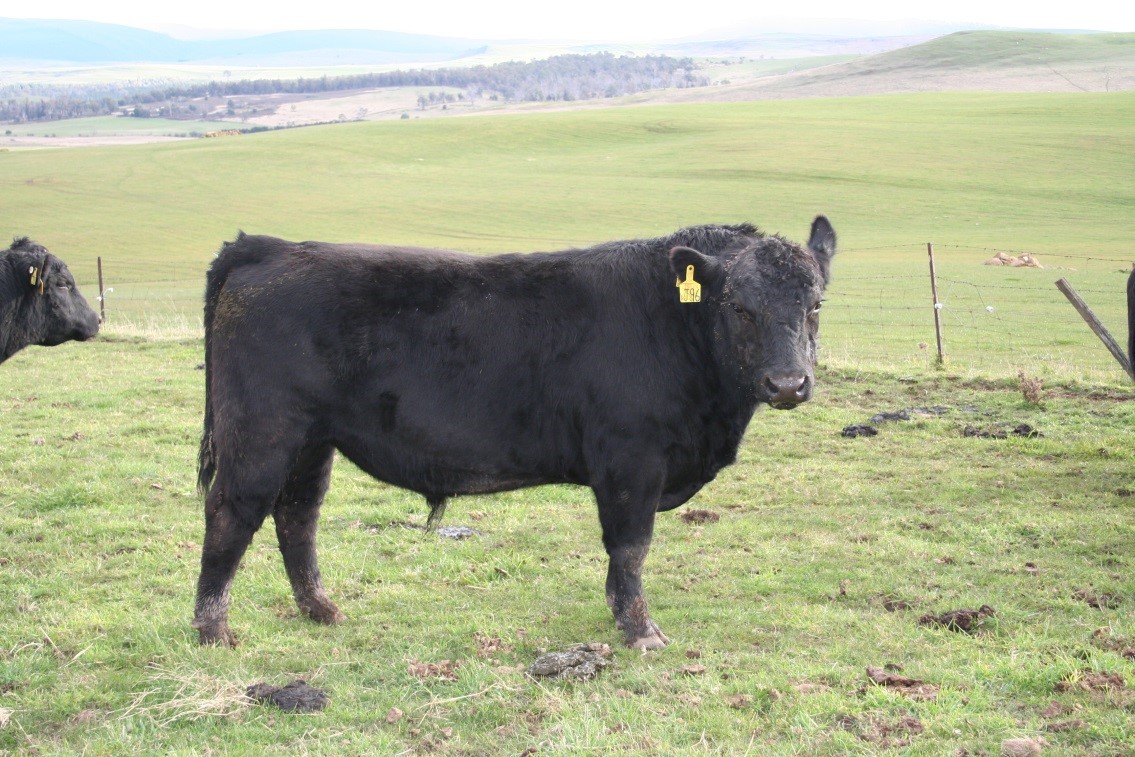

Price........... Purchaser..............................
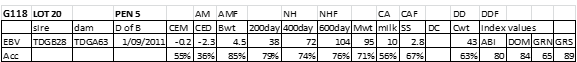
LOT 5
Price........... Purchaser..............................
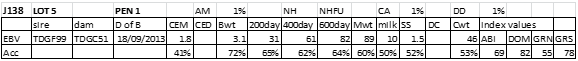
LOT 6
Price........... Purchaser..............................
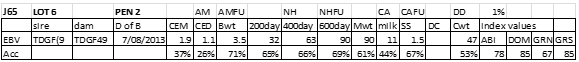
LOT 7
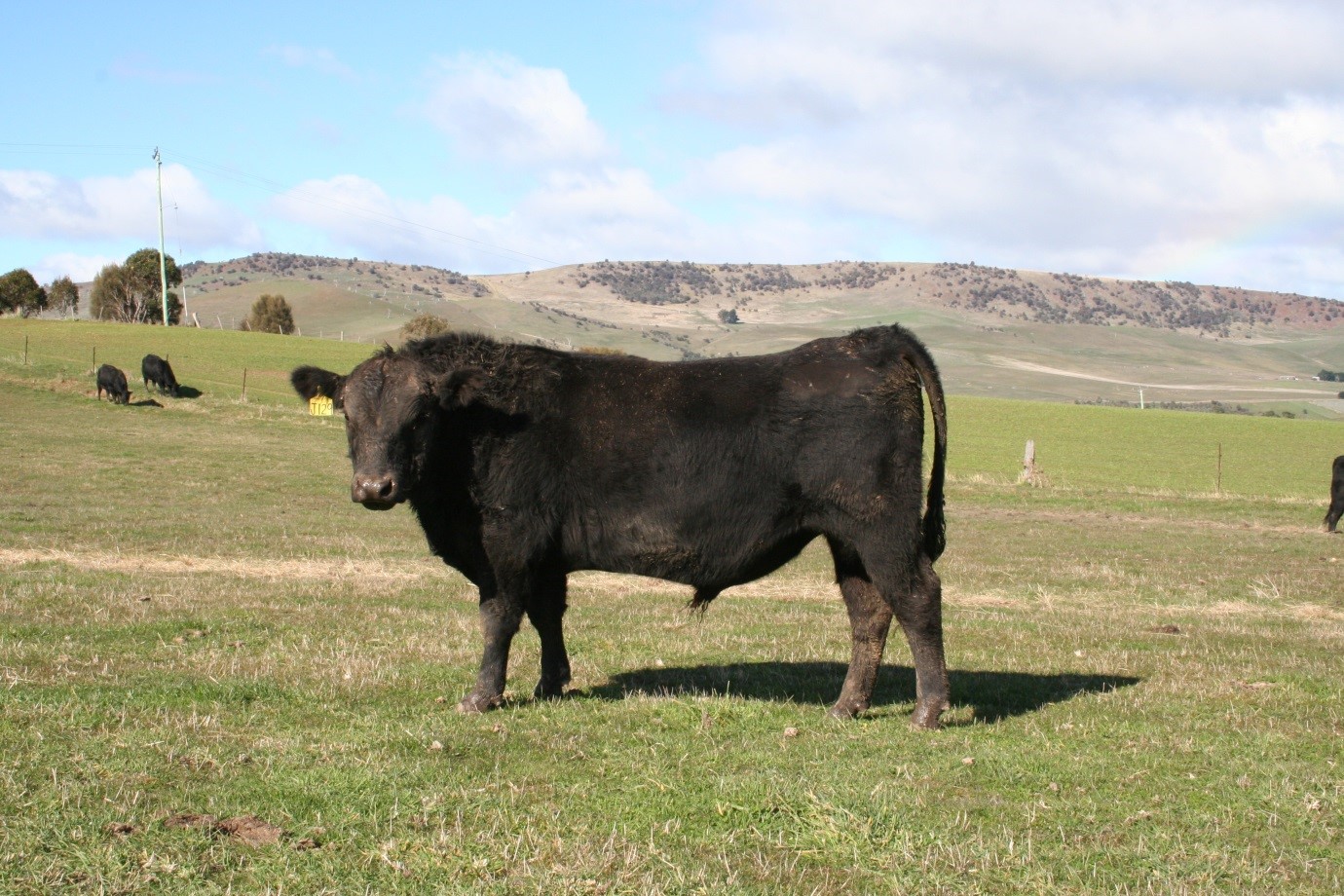

Price........... Purchaser..............................
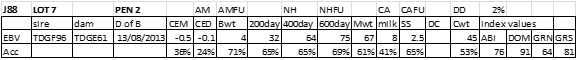
LOT 8
Price........... Purchaser..............................
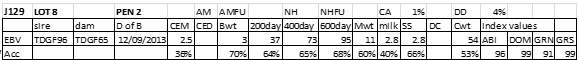
LOT 9
Price........... Purchaser..............................
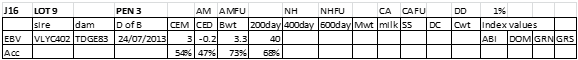
LOT 10
Price........... Purchaser..............................
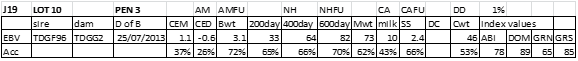
LOT 11
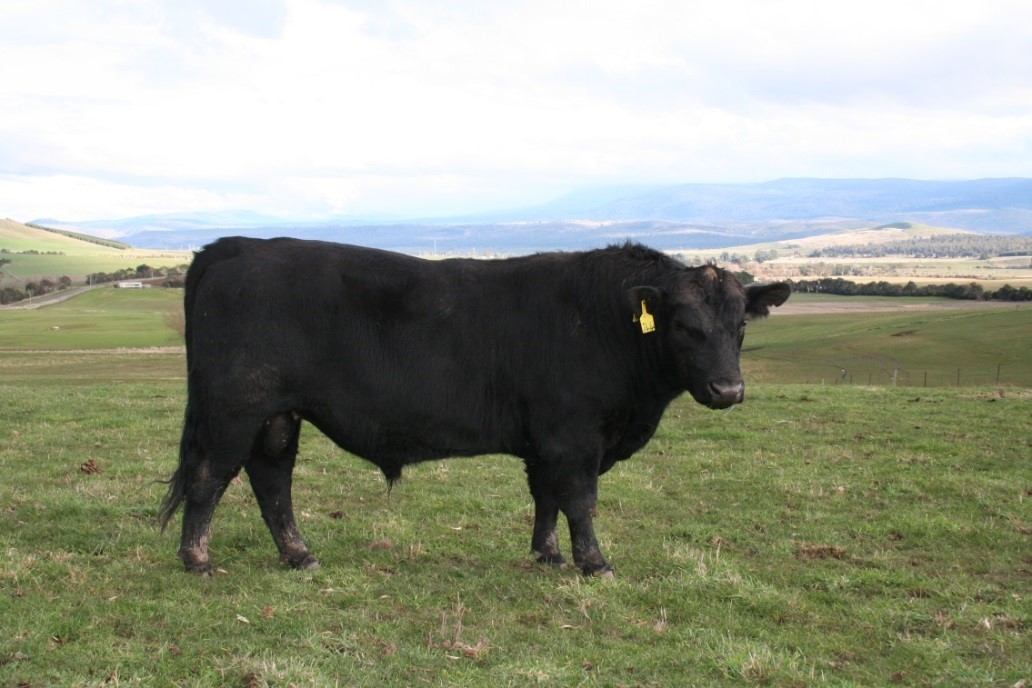

Price........... Purchaser..............................
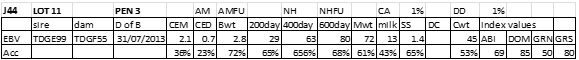
LOT 12
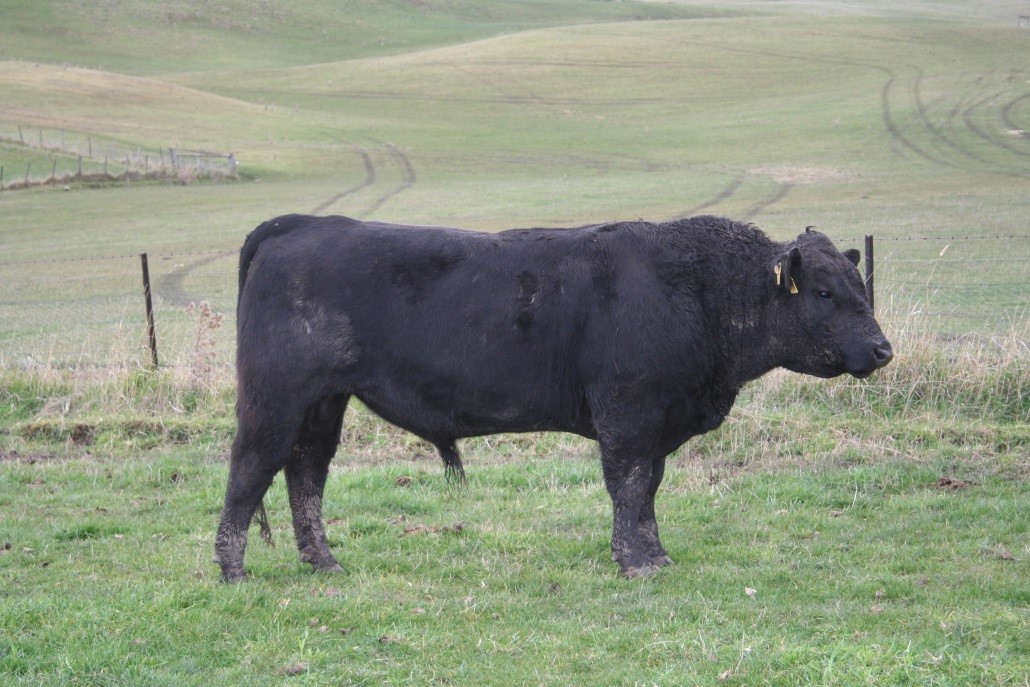

Price........... Purchaser..............................
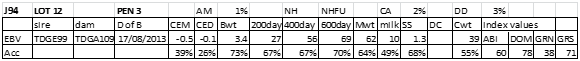
LOT 13
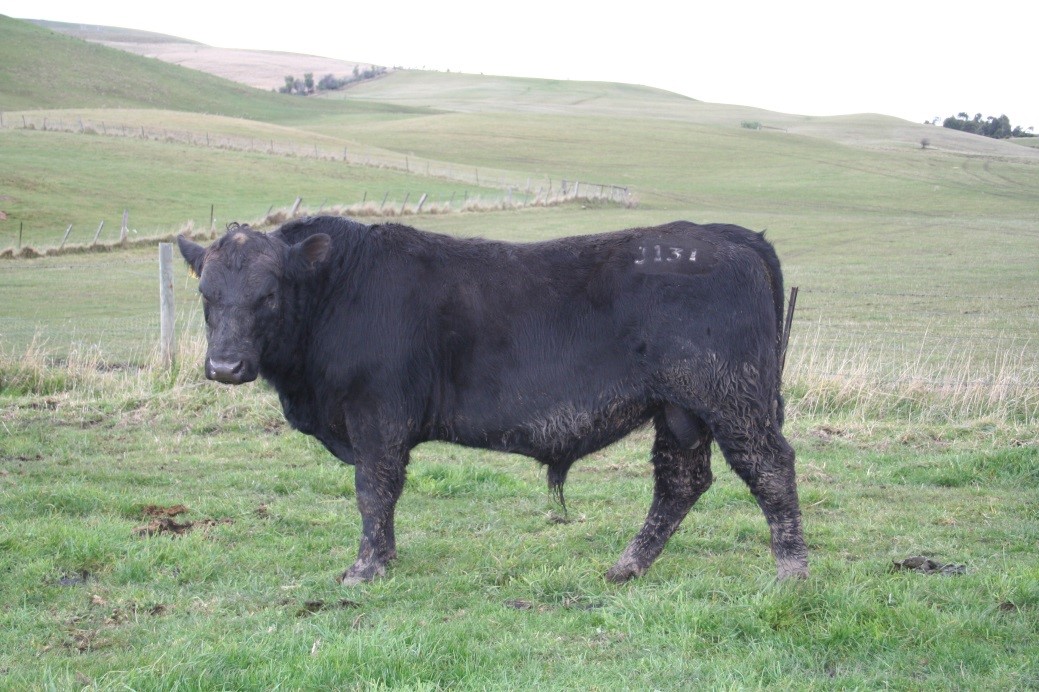

Price........... Purchaser..............................
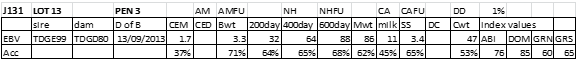
LOT 14
Price........... Purchaser..............................
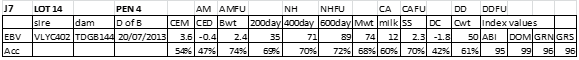
LOT 15
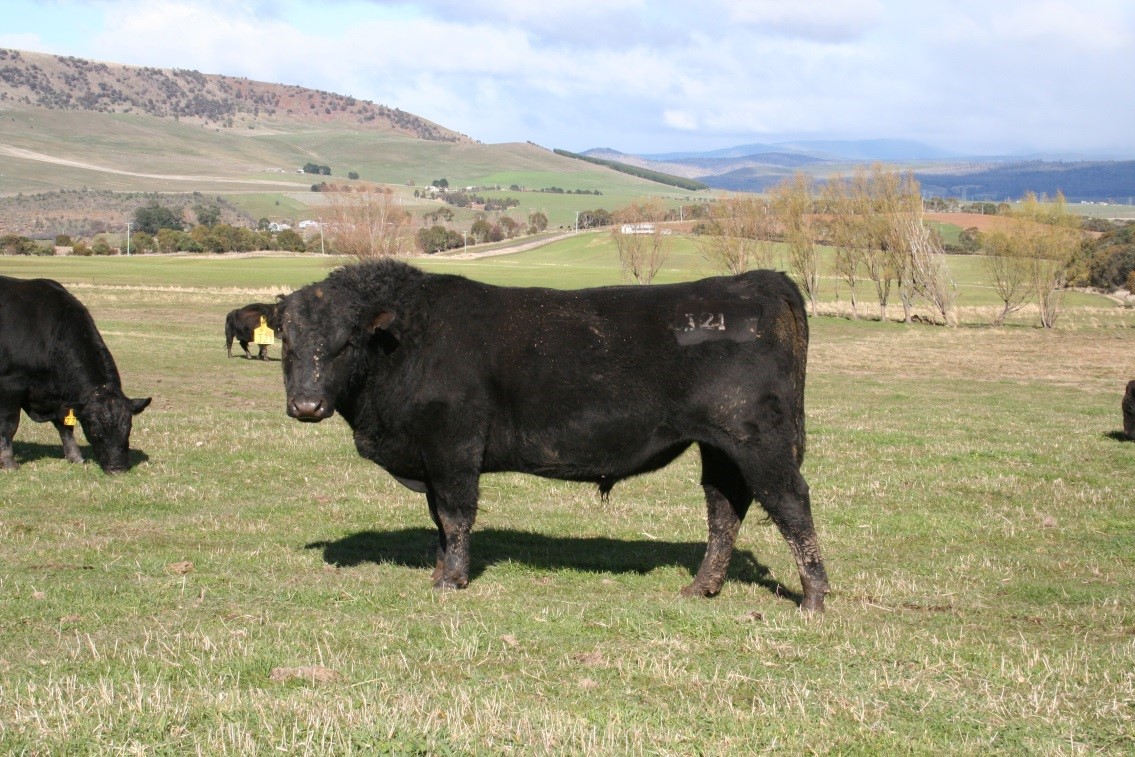

Price........... Purchaser..............................
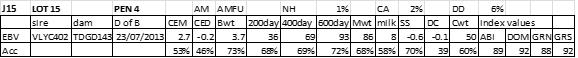
LOT 16
Price........... Purchaser..............................
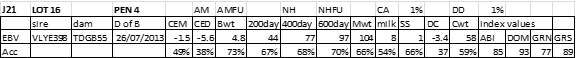
LOT 17
Price........... Purchaser..............................
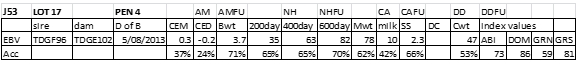
LOT 18
Price........... Purchaser..............................

LOT 19
Price........... Purchaser..............................
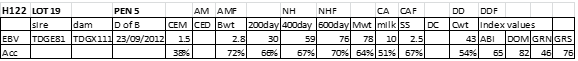
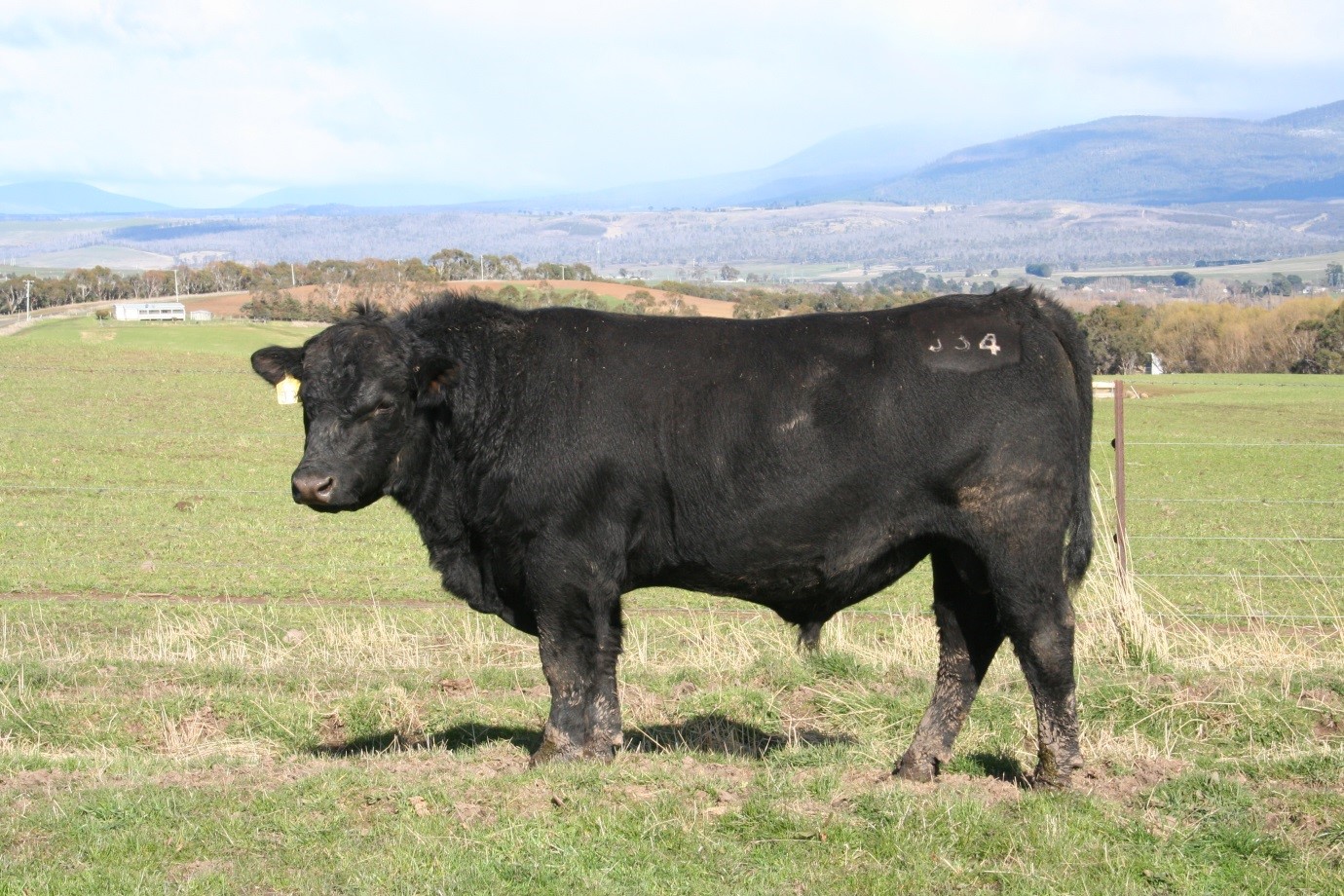
LOT 20
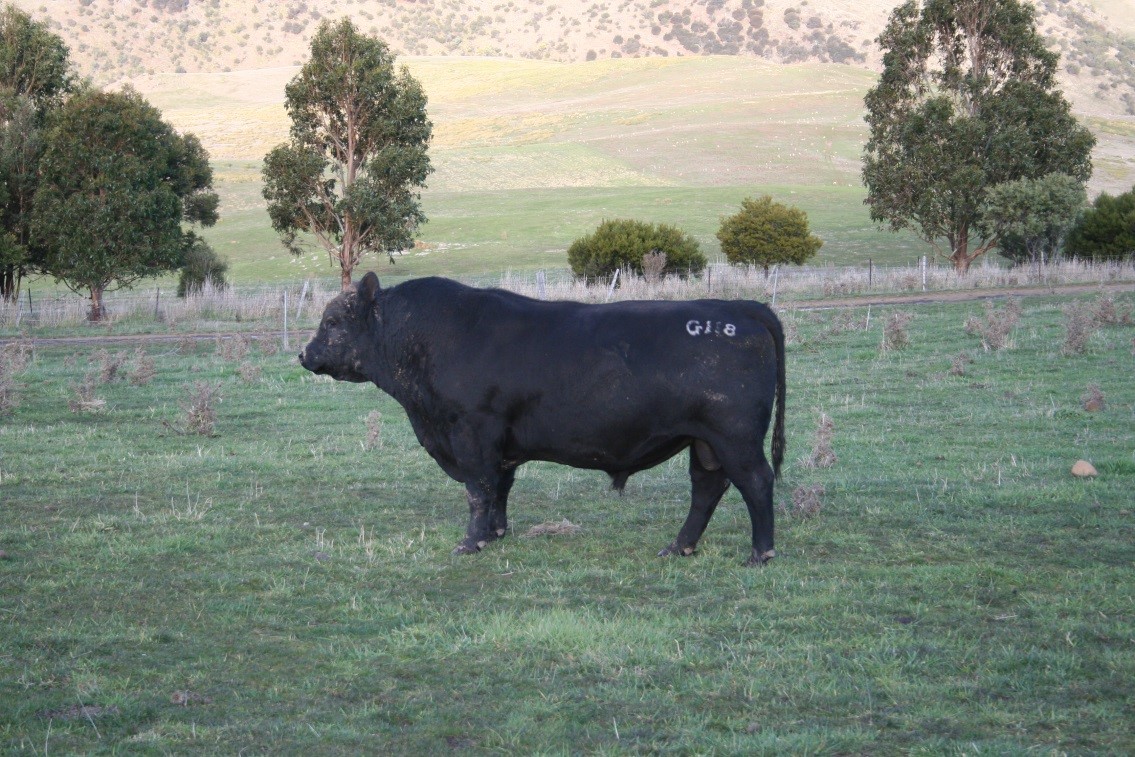

Price........... Purchaser..............................